The discovery of microRNA has revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation, a groundbreaking achievement credited to Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun and his colleague Victor Ambros in the early 1990s. This pivotal research, conducted on the C. elegans roundworm, revealed complex mechanisms that control gene expression and protein translation, which has widespread implications for biology and medicine. Ruvkun’s work, largely supported by NIH grants, laid the foundation for numerous applications, including innovative therapies aimed at treating diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s. As the interest in microRNA research expanded, it became clear that these tiny molecule regulators play critical roles across various organisms, igniting a surge of scientific inquiry. Today, the significance of microRNA is not only recognized within the academic community, but it also galvanized advancements in biotechnology, earning Ruvkun the 2024 Nobel Prize in physiology for his landmark discoveries.
The exploration of small RNA molecules, specifically microRNA, represents a significant breakthrough in the landscape of genetic science. Through meticulous research on the model organism C. elegans, scientists like Gary Ruvkun have illuminated the intricate processes of gene regulation and expression. This area of study has garnered widespread interest, drawing in funding predominantly from institutes such as the NIH, thereby propelling forward our understanding of how these miniaturized RNAs influence developmental and physiological functions. As the foundational work on microRNA continues to unfold, it opens doors to revolutionary therapeutic strategies for various diseases, showcasing its role as a cornerstone in the future of molecular biology and medicine.
The Impact of Gary Ruvkun’s Research on Gene Regulation
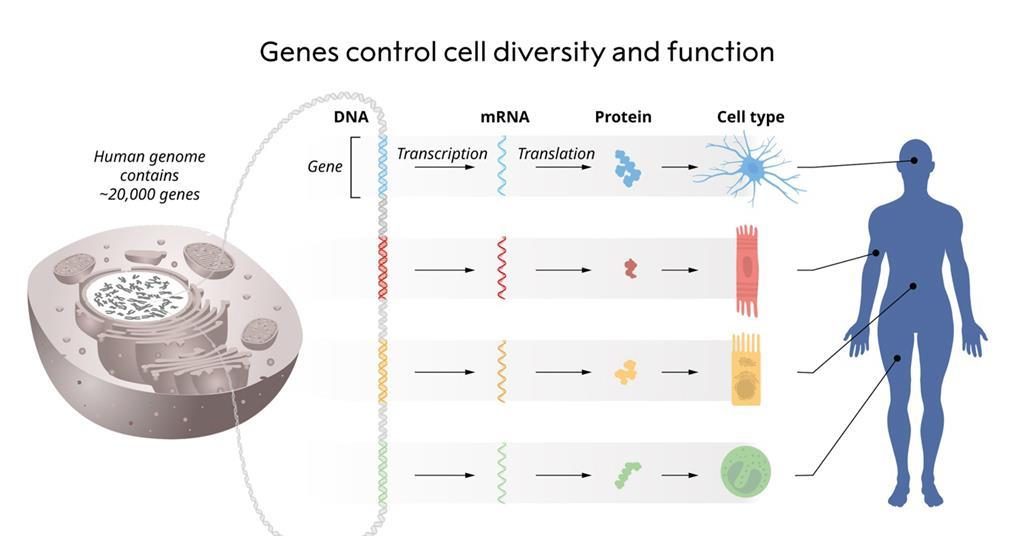
Gary Ruvkun’s pioneering work in the early 1990s on gene regulation has paved the way for significant advancements in molecular biology and genetics. His discovery of microRNA in the *C. elegans* roundworm highlighted a previously unknown layer of genetic control, which is now recognized as vital for understanding the complexities of gene expression. MicroRNAs are short RNA molecules that play essential roles in regulating gene activity, influencing various biological processes from development to disease pathology. By uncovering this dimension of gene regulation, Ruvkun and his colleagues set the foundation for innovations in therapeutic strategies targeting RNA.
The initial skepticism surrounding Ruvkun’s findings transformed over the decades into widespread recognition of microRNAs’ importance. As more researchers began to explore the implications of his work, the scientific community acknowledged that microRNA regulation is crucial not just in *C. elegans*, but across multiple organisms, including humans. This shift in perception has been critical in driving further research into gene regulation and has significantly influenced advances in biotechnology. Consequently, Ruvkun’s vision has contributed to the growing field of genetics, inspiring new studies supported by NIH grants that continue to explore how these tiny RNAs are integral to various biological functions.
MicroRNA Discovery: Revolutionizing Therapeutics
The discovery of microRNAs has profoundly altered the landscape of therapeutic development, particularly in fields such as oncology and cardiology. Researchers are now harnessing the regulatory capabilities of these small RNA molecules to create novel treatments aimed at diseases like cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s. Clinical trials are currently evaluating therapies that leverage microRNA modulation, with the goal of correcting dysfunctional gene expression associated with these diseases. This shift reflects an increasing appreciation of microRNAs as potential targets for innovative medical interventions.
Furthermore, companies like Alnylam Pharmaceuticals have capitalized on the foundations laid by Ruvkun’s research, specializing in RNA interference therapeutics. By developing drugs that specifically target microRNAs and other RNA molecules, these firms exemplify how federal funding and basic scientific research can lead to commercial applications with the potential to drastically improve patient outcomes. This evolution from academic discovery to practical application underscores the significance of sustained investment in scientific research, particularly when examining how microRNA discovery can lead to cutting-edge advancements in medicine.
The Role of NIH Grants in Advancing MicroRNA Research
National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants have played a pivotal role in the support and advancement of Gary Ruvkun’s research and the broader field of microRNA investigation. Over the past four decades, much of Ruvkun’s work has been underpinned by federal funding, which has provided essential resources for researchers exploring the intricacies of gene regulation through microRNAs. As Ruvkun himself noted, this financial support has been crucial, enhancing the capabilities of smaller labs to conduct high-impact research without the overwhelming pressures that come with commercial funding.
The investment made through NIH grants not only fosters groundbreaking discoveries but also supports the next generation of scientists, ensuring that talented individuals can pursue careers in research without immediate financial burdens. As the relevance of microRNA in various biological processes becomes more recognized, the demand for federal backing has increased. This trend emphasizes the importance of continued funding in scientific fields, particularly as researchers aim to unravel the complexities of gene regulation and its implications for human health and disease.
The Evolution of MicroRNA Research Since 1992
Since the initial discovery of microRNAs in 1992, the field has evolved dramatically, marking a journey filled with both challenges and breakthroughs. Initially met with skepticism, Ruvkun and Ambros’s findings were seen as niche interests; however, the growing understanding of the ubiquitous roles played by these tiny RNA molecules has propelled microRNA research into the spotlight. The gradual acceptance and excitement from the scientific community have led to increased collaborative efforts and multidisciplinary approaches that accelerate discoveries related to gene regulation.
In recent years, the accumulation of evidence supporting the diverse roles of microRNAs has sparked a surge of interest across various scientific disciplines, from molecular biology to clinical medicine. Researchers have demonstrated that microRNAs are not only crucial for regulating gene expression but also serve as biomarkers for numerous diseases. As scientists strive to uncover the functional roles of these molecules in different contexts, the original discoveries by Ruvkun and his colleagues have laid a solid foundation for an expansive field of study that continues to flourish.
MicroRNAs: From Basic Research to Clinical Trials
The transition of microRNA research from foundational biology to clinical application is a testament to the value of basic research principles. Early discoveries made by Ruvkun provided insight into the regulatory mechanisms of gene expression, which have now caught the attention of clinical researchers pursuing novel therapeutic avenues. The therapeutic potential of microRNAs has led to a growing focus on utilizing these molecules in clinical trials, indicating that the translation from bench to bedside is not only possible but increasingly becoming a reality in modern medicine.
Current studies exploring microRNA-based therapies are paving the way for innovative treatments for complex diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders. By harnessing the natural regulatory capabilities of microRNAs, researchers aim to develop strategies that can effectively modulate gene expression and restore normal cellular functioning. This clinical interest has not only revitalized enthusiasm for microRNA research but also reinforced the necessity of ongoing funding and collaborative efforts to explore the vast potential of these small molecules in therapeutic contexts.
Challenges Faced by Early MicroRNA Researchers
Despite the groundbreaking nature of Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros’s discovery of microRNAs, the early years of research were not without their challenges. Initial skepticism from the scientific community and limited understanding of the implications of microRNA regulation posed significant hurdles for both researchers and their findings. As the significance of microRNAs became more apparent, the investment needed to expand this research was only partly met by the funding landscape at the time, which often prioritized other burgeoning fields.
Navigating through the uncertainties, Ruvkun and others faced the challenge of convincing the broader biological community that their findings had implications beyond *C. elegans*. It required persistence and dedication to continue their experimentation while receiving relatively modest funding, primarily through NIH grants. The trials endured during this era have since underscored the importance of resilience in scientific research and the need for funding bodies to recognize and support new and potentially transformative pathways in gene regulation.
The Future of MicroRNA Research: Directions and Possibilities
As research into microRNAs expands, the future holds promising possibilities for unraveling the complexities of gene regulation. With the growing body of evidence supporting the role of microRNAs in various biological processes, researchers are increasingly focusing on understanding their precise mechanisms and interactions within cellular pathways. The insights gained from such investigations not only broaden our fundamental understanding of molecular biology but also open new avenues for therapeutic applications targeting specific diseases.
Moreover, with technological advancements in genomics and bioinformatics, researchers are better equipped to identify and characterize newly discovered microRNAs in multiple contexts. These developments signal an exciting era where the potential for personalized medicine based on microRNA profiling is within reach. Continued support from federal funding bodies, like the NIH, is essential for facilitating these research efforts and driving forward the next generation of breakthroughs that could stem from microRNA discovery and regulation.
The Interdisciplinary Nature of MicroRNA Research
The exploration of microRNAs has necessitated an interdisciplinary approach, bringing together biologists, clinicians, and bioinformaticians to form collaborations that cut across traditional scientific boundaries. This collaborative spirit has enhanced the understanding of microRNA functions across different organisms and their implications for human health. By integrating knowledge from various fields, researchers can work more effectively towards solving complex problems related to gene regulation and disease pathology.
Additionally, interdisciplinary research teams are critical for the development of innovative technologies aimed at harnessing microRNAs for therapeutic use. Such collaborations not only broaden the scope of investigation but also enhance the capacity for translation from basic research findings into clinical applications. This melding of expertise ultimately amplifies the impact of microRNA research and highlights the necessity for funding models that encourage collaborative projects across diverse scientific disciplines.
Funding and Its Role in Scientific Discovery
The role of funding, particularly from NIH grants, in supporting scientific discovery cannot be overstated. For a field like microRNA research, where early skepticism was prevalent, ongoing financial support has been vital in advancing understanding and innovation. Federal funding has allowed laboratory teams, including Ruvkun’s, to pursue ambitious research agendas without the looming pressure of yielding immediate commercial returns, which is often the case in industry-backed projects.
As the landscape of scientific funding evolves, it remains crucial to advocate for continued investment in fundamental research pathways like those explored by Ruvkun and others. The support provided through grants not only bolsters individual projects but also contributes significantly to public knowledge and healthcare advancements. Recognizing the essential nature of sustained funding will be key to addressing future challenges in genetics and gene regulation, ensuring that the momentum of discoveries continues for generations of researchers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is microRNA discovery and why is it important in gene regulation?
MicroRNA discovery refers to the identification and understanding of small RNA molecules that play a critical role in gene regulation. These molecules, first discovered by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros in 1992, regulate gene expression by targeting mRNA and controlling protein production, which is essential for understanding developmental biology and disease processes.
How did Gary Ruvkun contribute to the discovery of microRNA?
Gary Ruvkun, alongside Victor Ambros, pioneered the discovery of microRNA in the model organism *C. elegans*. Their groundbreaking research unveiled a novel layer of gene regulation, which ultimately earned them the 2024 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine, highlighting the significance of microRNAs in various biological processes.
What role does NIH grant funding play in microRNA research?
NIH grants have been pivotal in supporting microRNA research, providing essential funding for significant discoveries like those made by Gary Ruvkun. This federal support has enabled researchers to explore the biological functions of microRNAs and their applications in therapeutics for diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
What are some applications of microRNA in medicine?
MicroRNAs have numerous applications in medicine, particularly in developing therapies for conditions like heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s Disease, and Alzheimer’s. Ongoing clinical trials are exploring how microRNA-based treatments can effectively modulate gene expression and improve patient outcomes.
Why are microRNAs considered revolutionary in understanding gene regulation?
MicroRNAs are considered revolutionary because they reveal a complex regulatory layer in gene expression that was previously unknown. By controlling the translation of mRNAs, microRNAs have transformed how scientists understand developmental biology and gene regulation, marking a significant advancement in the field.
What was the initial reception of microRNA discoveries in the scientific community?
Initially, the discovery of microRNAs by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros was met with skepticism in the evolutionary biology community, as the relevance of their findings to other species, including humans, was not immediately recognized. Over time, as research expanded, the importance of microRNAs became widely acknowledged.
How many microRNAs are found in the human genome?
The human genome contains approximately 1,000 microRNAs, which play a vital role in regulating the majority of protein-producing genes. This extensive network of microRNAs is crucial for various biological processes, including development, cell differentiation, and response to environmental stimuli.
How do advancements in microRNA research influence biotechnology companies?
Advancements in microRNA research have positively influenced biotechnology companies, such as Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, which focus on RNA interference therapeutics. These companies leverage foundational research funded by NIH grants to innovate and develop new medical solutions for genetic diseases.
What are the implications of decreased federal funding for microRNA research?
A decrease in federal funding for microRNA research could hinder scientific progress and discourage young researchers from pursuing careers in science. As highlighted by Gary Ruvkun, continued investment in basic research is crucial for maintaining the United States’ position as a leader in scientific discovery and technological advancement.
How has the interest in microRNA research changed over the years?
Interest in microRNA research has significantly increased since its initial discovery, expanding from a niche community of RNA researchers to a broader interest across various fields, including evolutionary biology and medicine. This growth is reflected in the increasing attendance at scientific meetings and the range of applications being explored.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in 1992, leading to their Nobel Prize in 2024. |
| Their research focused on gene regulation in the C. elegans roundworm, showing significance in other species including humans. |
| Initial interest was limited, mainly among RNA researchers and the ‘worm community’. |
| Therapies based on microRNAs for various diseases are currently in clinical trials. |
| MicroRNAs play essential roles in gene expression, with about 1,000 microRNAs controlling human protein-producing genes. |
| Ruvkun’s lab research has been largely funded by federal grants, emphasizing the importance of this funding for scientific development. |
| Ruvkun advocates for continued federal investment in science to maintain U.S. leadership in innovation and research. |
Summary
MicroRNA discovery is a groundbreaking achievement in genetics that has reshaped our understanding of gene regulation. The discovery by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros not only highlighted the importance of microRNAs in developmental biology but also opened new avenues for therapeutic interventions in various diseases. With ongoing research and clinical trials, the implications of microRNA continue to expand, confirming their vital role in health and medicine. Continued support for such innovative research is essential to ensure advancements in this promising field.